(note: annoyingly this method did not keep accurate references…)
The confluence of new machine learning (ML) methods, multimodal imaging, and medicine marks a pivotal advancement in healthcare. This synergistic integration promises to significantly enhance diagnostic precision, facilitate personalized treatment strategies, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. While traditional medical imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, PET, and ultrasound, offer invaluable insights, their individual perspectives often present an incomplete view of complex biological phenomena. Multimodal imaging addresses this inherent limitation by integrating data from a diverse array of sources, encompassing various imaging modalities, genomic information, electronic health records (EHRs), and clinical notes. The true transformative potential of this integration is unleashed through advanced machine learning algorithms, which are uniquely capable of processing, fusing, and interpreting these high-dimensional and heterogeneous datasets to reveal subtle patterns and generate robust predictions beyond human analytical capacity.
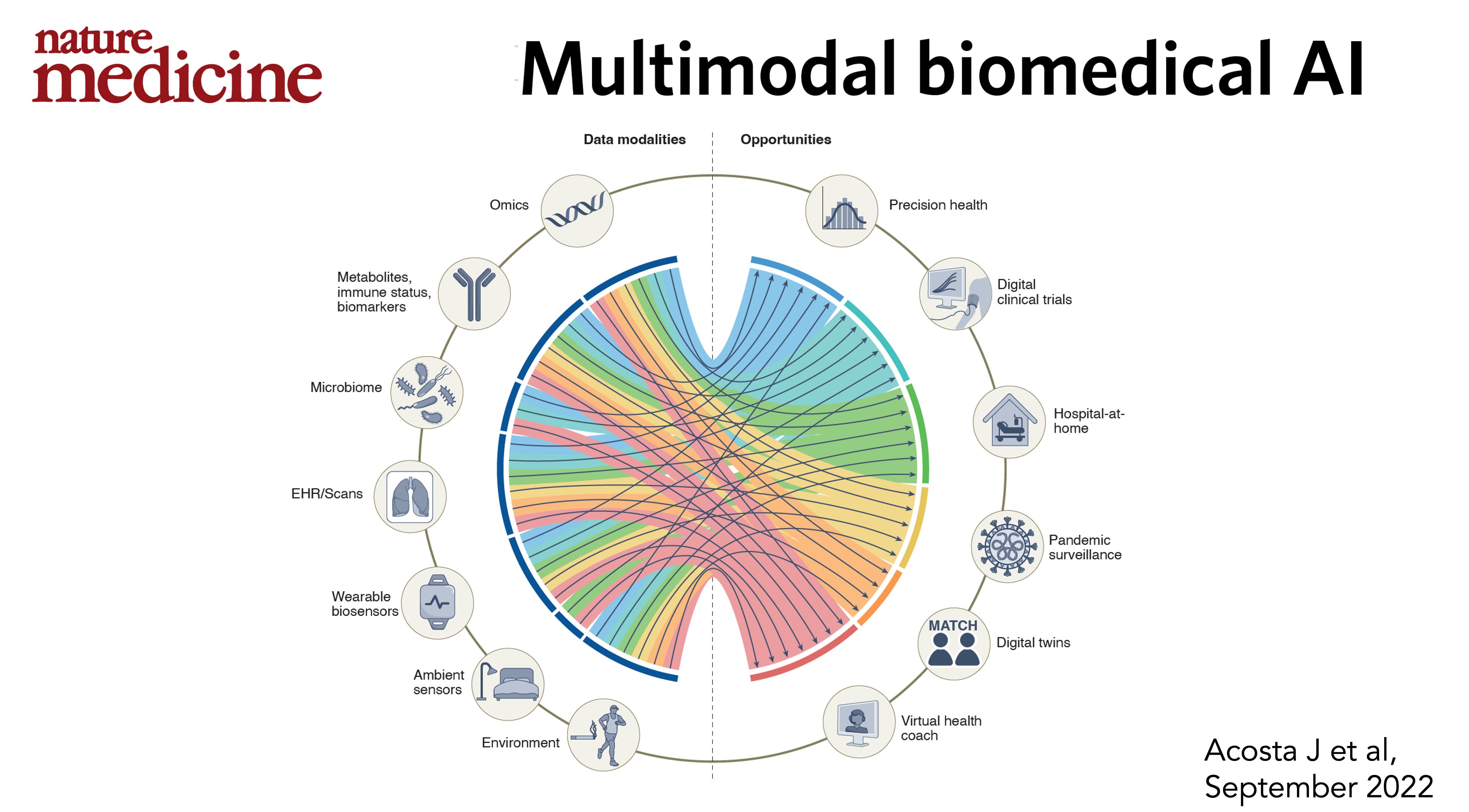
Figure 1: Multimodal AI for medicine, simplified, illustrating the integration of diverse data types to achieve precision medicine goals. (Source: Topol 2023)
The profound synergy between multimodal data and artificial intelligence (AI) is instrumental in propelling the field of precision medicine forward. By meticulously combining information from distinct imaging modalities (e.g., anatomical and functional scans), genetic profiles, and comprehensive patient histories, ML models can construct holistic and nuanced patient representations. This integrated approach facilitates more accurate disease detection, precise stratification of patient risk, and robust prediction of treatment responses. Machine learning algorithms, spanning cutting-edge deep learning architectures like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformers, as well as more established statistical methods, are adept at identifying intricate correlations across different data types, thereby empowering clinicians with more informed decision-making capabilities.
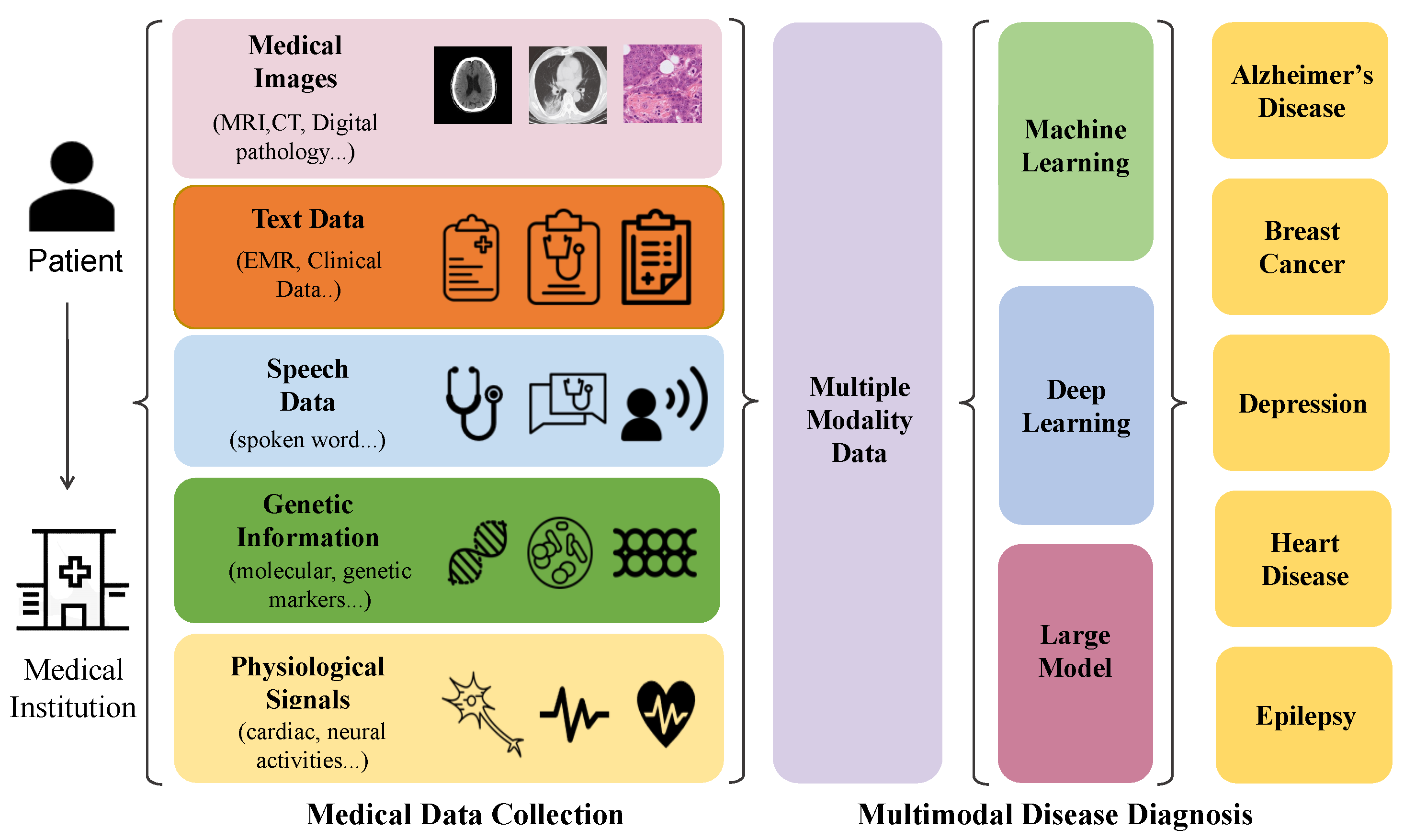
Figure 2: Illustrates the comprehensive synergy between multi-modal data and AI for enhancing precision medicine. (Source: Asif et al. 2024)
The application of machine learning within multimodal medical imaging is remarkably broad and impactful across various medical disciplines. In the context of neurological disorders, for instance, the integration of MRI for structural information, fMRI for functional brain activity, and PET for metabolic processes, further augmented by ML, can yield a significantly more precise diagnosis and prognosis for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease or epilepsy. Similarly, in cardiology, fusing echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and a multitude of clinical parameters allows sophisticated ML models to predict heart failure progression or identify patients at elevated risk for adverse cardiac events. ML models are particularly invaluable in navigating the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of multimodal datasets, enabling clinicians to transcend the limitations of isolated data points and achieve a more integrated understanding of disease pathophysiology.

Figure 3: Overview of machine learning’s role in processing and interpreting multimodal medical imaging data. (Source: Zhang 2017)
Oncology represents another significant domain that profoundly benefits from multimodal AI. The diagnosis, staging, and intricate treatment planning for cancer often necessitate a combination of imaging data (e.g., CT, MRI, PET), histopathology reports, genomic sequencing results, and circulating biomarkers. Machine learning methods are adept at integrating these diverse data streams to accurately identify tumor subtypes, predict patient response to specific chemotherapies or immunotherapies, and monitor disease progression with unprecedented accuracy. For example, in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, multimodal AI can provide crucial assistance in refining diagnosis and prognosis by simultaneously considering various clinical and imaging features, thereby guiding the development of more personalized and effective treatment regimens.

Figure 4: Highlights the specific applications of multimodal AI in improving diagnosis and prognosis for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. (Source: Hao, Li, and Zhong 2024)
The continuous advancement of this burgeoning field is propelled by diligent research and development efforts spanning academic institutions and industrial laboratories worldwide. Researchers are persistently exploring novel ML architectures, sophisticated data fusion techniques, and interpretable AI methods to address persistent challenges such as data heterogeneity, the presence of missing data, and potential model bias. A concerted focus is also directed towards developing robust and generalizable AI models that can be seamlessly integrated into existing clinical workflows, meticulously ensuring adherence to ethical considerations and regulatory compliance. These ongoing innovations are absolutely critical for translating cutting-edge research into tangible, life-changing benefits for patients, further solidifying the indispensable role of multimodal AI as a cornerstone of future medical practice.
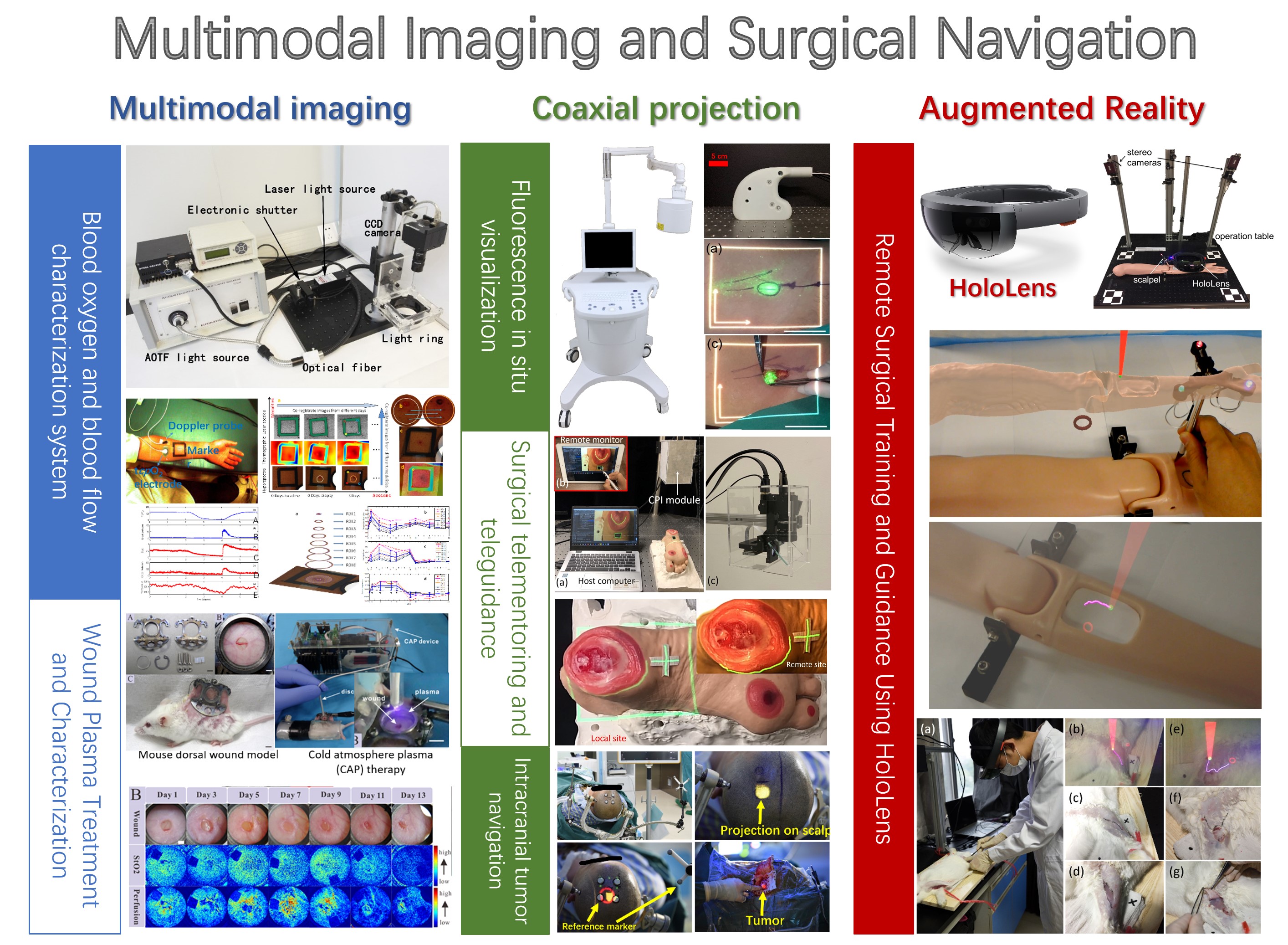
Figure 5: Represents research efforts in the field of multimodal biomedical imaging and therapy. (Source: University of Science and Technology of China n.d.)
Bibliography
Asif, Areeba, Kashif Iqbal, Anila Basheer, Asif Ali, Nabeela Anjum, Muhammad Jawad Aslam, Abdul Raouf Khan, and Muhammad Usman Akram. “A Comprehensive Review on Synergy of Multi-Modal Data and AI for Enhancing Precision Medicine: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.” Bioengineering 11, no. 2 (2024): 219. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/11/2/219.
Hao, Yanlong, Longjun Li, and Jianhong Zhong. “Applications of Multimodal Artificial Intelligence in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Diagnosis and Prognosis.” Biomedicines 12, no. 8 (2024): 1753. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4426/12/8/1753.
Topol, Eric. “Multimodal AI for medicine, simplified.” Ground Truths (blog), March 17, 2023. https://erictopol.substack.com/p/multimodal-ai-for-medicine-simplified.
University of Science and Technology of China. “Lab for Multimodal Biomedical Imaging and Therapy (MBIT).” Accessed October 26, 2023. https://www.mbit.ustc.edu.cn/.
Zhang, Yalin. “Machine Learning in Multimodal Medical Imaging.” In Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, 1–32. Cham: Springer, 2017.

Leave a Reply